
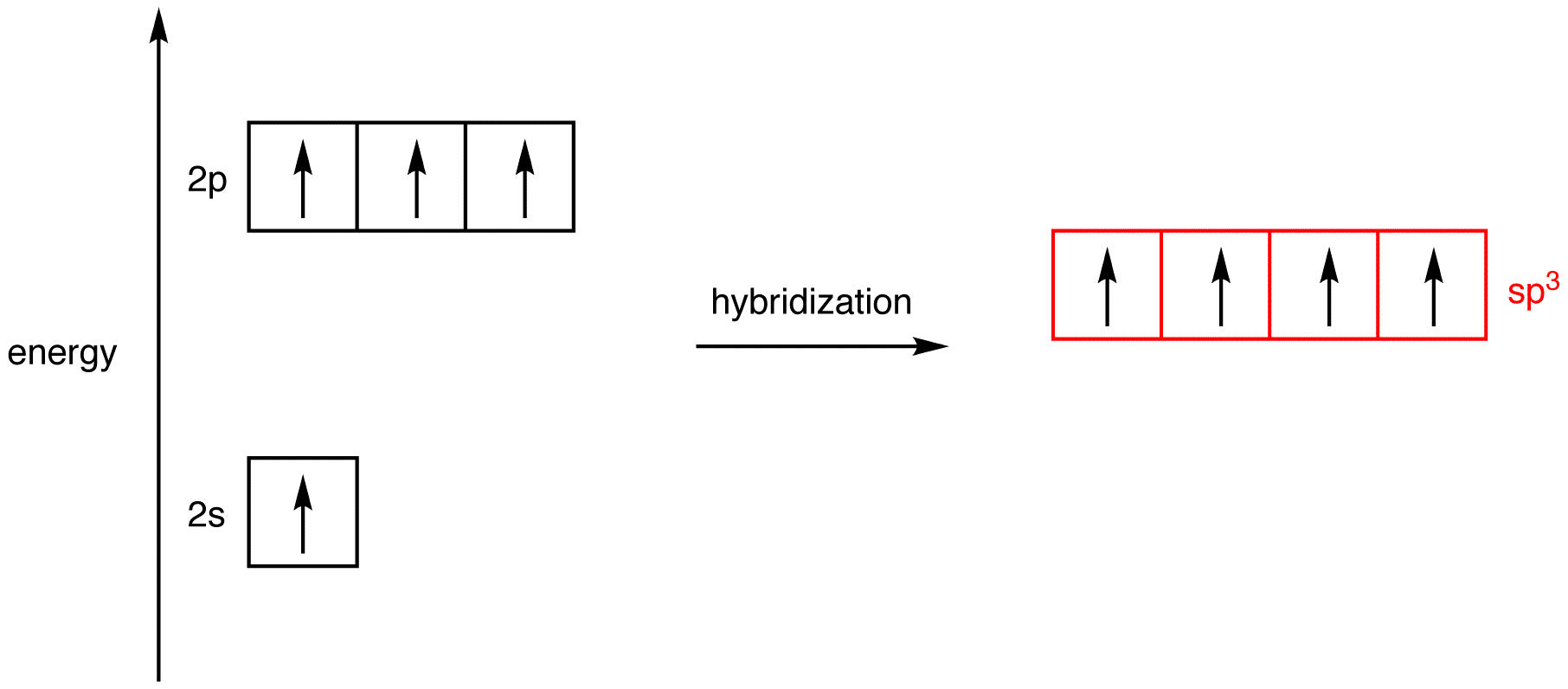
In order to understand why an orbital will engage in hybridization, we need to first look at the electron configuration. HYPERVALENCY OF PHOSPHORUS Since phosphorus ( 'P' , atomic number 15 ) is on the third period of the periodic table , it has access to orbitals of principal quantum number n \mathbf(3). You can count these up and see that the number of orbitals used in the hybridization equal the number of electron groups around the central atom.
Of lone pairs STEP-5: Assign hybridization and shape of moleculeNow, based on the steric number, it is possible to get the type of hybridization of the atom. Boron atom gets negative charge when it accepts a lone pair from hydride ion, H - in borohydride ion, BH 4 - STEP-4: Calculate the steric number:Steric number = no. Nitrogen atom in ammonium ion, NH 4 + gets positive charge since it donates a pair of electrons to H + ion.If it receives a lone pair, a negative charge is acquired. Of bonds (including both σ & π bonds) formed by concerned atom.C = charge on the atom (take care: it may not be the charge on entire molecule or ionic species).Note: When the concerned atom makes a dative bond with other atoms, it may acquire positive or negative charge depending on whether it is donating or accepting the lone pair while doing so respectively.If it donates a lone pair, a positive charge is accumulated. Before bond formation).B = no. Of valence electrons in the concerned atom in free state (i.e.

Therefore it forms 3 bonds with three hydrogen atoms. The bond angle is 19 o28'.DETERMINING THE HYBRIDIZATION OF NITROGEN IN AMMONIA, NH 3 STEP-1: Write the Lewis structureThe valency of nitrogen is 3. Of lone pairs = 4 + 0 = 4 STEP-5: Assign hybridization and shape of moleculeThe hybridization of carbon in methane is sp 3.This molecule is tetrahedral in structure as well as in shape, since there are no lone pairs and the number of σ-bonds is equal to the steric number. STEP-4: Calculate the steric number of carbon atom:Steric number = no. STEP-3: Calculate the number of lone pairsThe number of lone pairs on carbon atom = (v - b - c) / 2 = (4 - 4 - 0) / 2 = 0.Note: There are 4 valence electrons in the carbon atom before bond formation. Also remember that the valency of hydrogen is one.STEP-2: Calculate the number of sigma (σ) bondsSince carbon is attached to four hydrogen atoms, the number of σ-bonds is equal to 4.
Of lone pairs = 3 + 1 = 4 STEP-5: Assign hybridization and shape of moleculeNitrogen in ammonia undergoes sp 3 hybridization.The structure of this molecule is based on tetrahedral geometry with one lone pair occupying a corner.The steric number is not equal to the number of σ-bonds.Hence the shape is pyramidal (consider only the arrangement of only bonds and atoms in space).Note: The bond angle is not equal to 109 o28'. STEP-4: Calculate the steric number of nitrogen atom:Steric number = no. STEP-3: Calculate the number of lone pairsThe number of lone pairs on nitrogen atom = (v - b - c) / 2 = (5 - 3 - 0) / 2 = 1.Note: There are 5 valence electrons in the nitrogen atom before the bond formation. Hence the number of sigma bonds is equal to 3.
STEP-4: Calculate the steric number of central atom:Steric number = no. STEP-3: Calculate the number of lone pairsThe number of lone pairs on xenon atom = (v - b - c) / 2 = (8 - 4 - 0) / 2 = 2.Note: Xenon belongs to 18th group (noble gases). STEP-2: Calculate the number of sigma (σ) bondsThe number of sigma bonds formed by xenon is four since it is bonded to only four fluorine atoms.Note: The valency of fluorine is one. STEP-4: Calculate the steric number of central atom:Structure is based on tetrahedral geometry.Shape is also tetrahedral since there are no lone pairs.FINDING THE HYBRIDIZATION AND SHAPE OF XeF 4 STEP-1: Write the Lewis structureSkip this step. STEP-3: Calculate the number of lone pairsThe number of lone pairs on nitrogen atom = (v - b - c) / 2 = (5 - 4 - 1) / 2 = 0. STEP-2: Calculate the number of sigma (σ) bondsThe number of sigma bonds formed by nitrogen is 4 since it is bonded to 4 hydrogen atoms.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
